FreeXmlToolkit
XML Digital Signatures
Last Updated: November 2025 Version: 1.0.0
This tool lets you digitally sign XML documents and verify signatures. A digital signature proves that a document is authentic and hasn’t been changed.
Overview
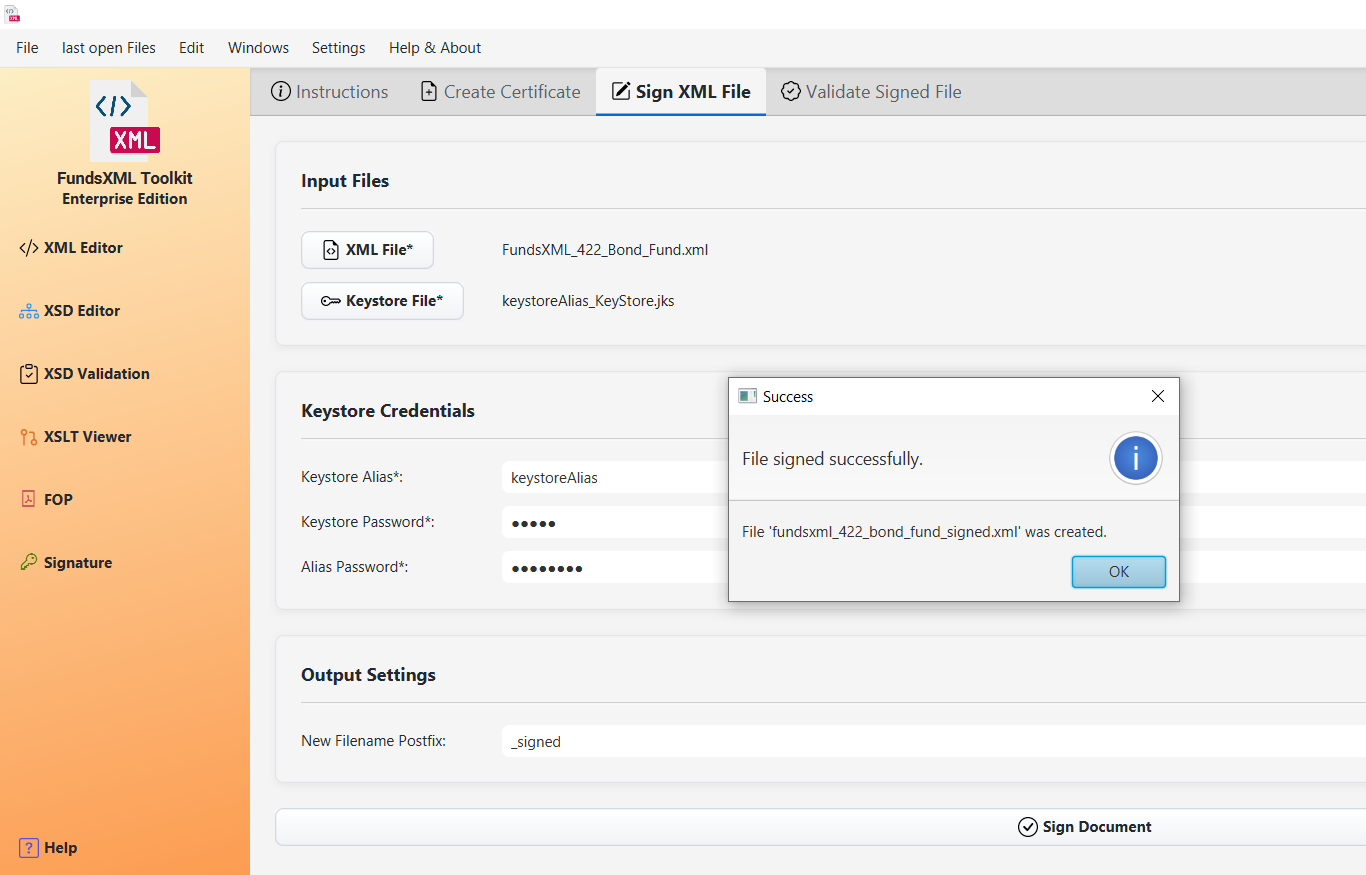 The digital signature interface
The digital signature interface
What Can You Do?
- Create Certificates - Generate your own digital ID
- Sign Documents - Add a digital signature to XML files
- Verify Signatures - Check if signed documents are valid
1. Create a Certificate
Before signing documents, you need a digital certificate (like a digital ID card).
 Screenshot placeholder: Certificate creation form
Screenshot placeholder: Certificate creation form
How to Create a Certificate
- Go to the “Create Certificate” tab
- Fill in your details:
- Name
- Organization
- Country
- Set a password for the certificate
- Click “Create”
- Save the keystore file (
.jks) - you’ll need this for signing
Important: Remember your password! You’ll need it every time you sign a document.
2. Sign an XML Document
 Screenshot placeholder: Document signing interface
Screenshot placeholder: Document signing interface
How to Sign a Document
- Go to the “Sign XML File” tab
- Select the XML file you want to sign
- Select your keystore file (
.jks) - Enter your passwords
- Click “Sign”
- A new signed XML file is created
The signed file includes the original content plus a digital signature.
3. Verify a Signature
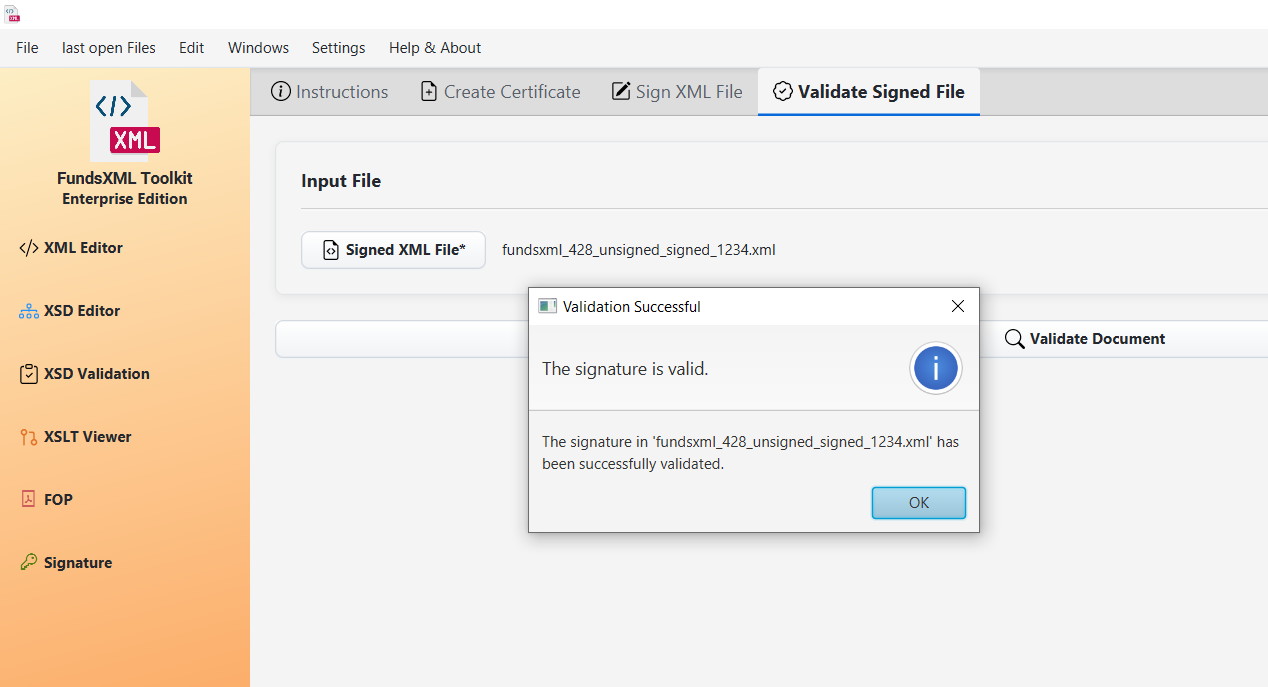 Verifying a signed document
Verifying a signed document
How to Verify a Signature
- Go to the “Validate Signed File” tab
- Select the signed XML file
- Click “Validate”
- See the result: Valid or Invalid
What the Verification Checks
| Check | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Authenticity | The signature was created by the certificate holder |
| Integrity | The document hasn’t been changed since signing |
Expert Mode (Advanced)
For users who need more control, the Expert Mode offers additional options:
 Screenshot placeholder: Expert mode interface
Screenshot placeholder: Expert mode interface
Advanced Features
- Different encryption methods - Choose from various security levels
- Custom certificate options - Set validity periods and extensions
- Detailed validation - Get comprehensive technical reports
- Advanced signature types - Choose how the signature is embedded
Tips
- Keep your keystore safe - It’s your digital identity
- Remember your passwords - They cannot be recovered
- Signed files are new files - The original is not modified
- Check validity regularly - Signatures can expire
Common Questions
What if I lose my password?
Unfortunately, passwords cannot be recovered. You’ll need to create a new certificate.
What file formats are supported?
- Input: XML files, JKS keystores
- Output: Signed XML files with embedded signatures
Can I sign PDFs?
No, this tool is specifically for XML documents.
Navigation
| Previous | Home | Next |
|---|---|---|
| PDF Generator (FOP) | Home | Auto-Completion |
| All Pages: XML Editor | XML Features | XSD Tools | XSD Validation | XSLT | FOP/PDF | Signatures | IntelliSense | Schematron | Favorites | Templates | Tech Stack | Licenses |